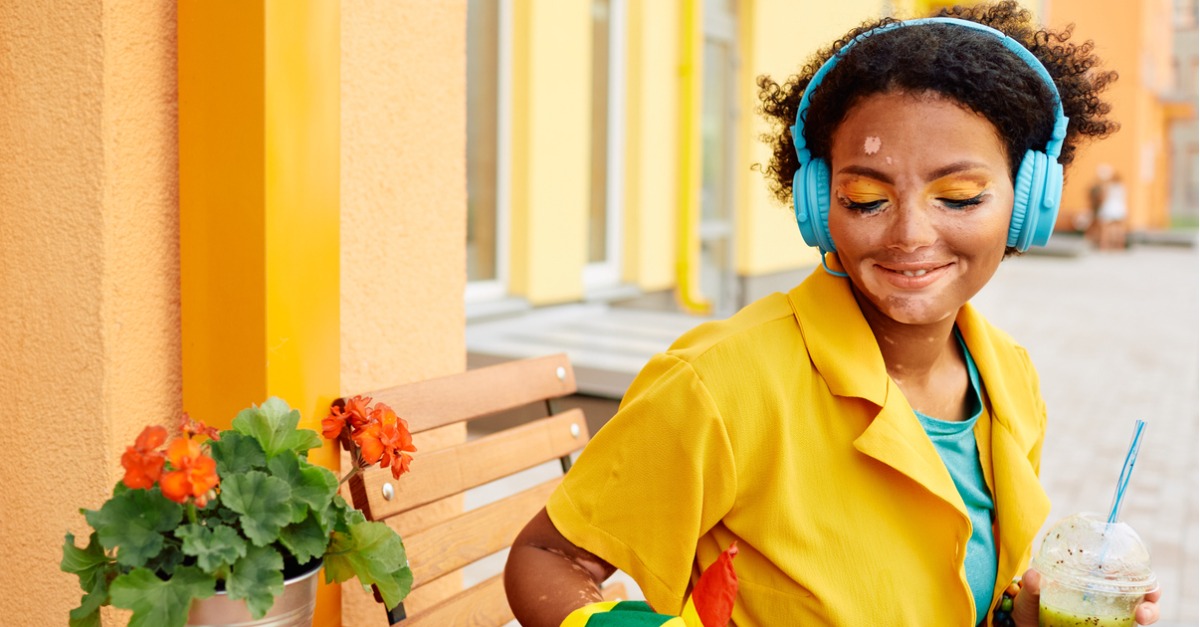
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition in which melanocytes (the cells responsible for creating pigment) are destroyed. This develops milky white skin patches, which are often more pronounced on people with darker skin. Some familiar faces who have vitiligo include the model Winnie Harlow and the late King of Pop, Michael Jackson.
If you suspect you might have vitiligo, here’s what you should know.
What Are the Symptoms?
Symptoms of vitiligo vary by type. In nonsegmental or generalized vitiligo, the white patches appear symmetrically on both sides of the body. In this most common type of vitiligo, pigment loss can happen quickly and may cover large portions of skin.
Segmental vitiligo, on the other hand, is rare and occurs when white patches appear only on one side of the body. For example, pigment loss may only appear on one leg, arm, or side of the face. Typically, the condition progresses for a specific period of time, such as one to two years, and then stops completely.
While these milky patches typically develop first on the face, hands, and near the genitals, they can also develop elsewhere such as on the knees or even the torso. According to the Mayo Clinic, vitiligo may also cause premature whitening of the hair, including on the scalp and facial hair. The mucous membranes inside the mouth and nose may also lose their color. It can develop at any age but tends to appear before the age of 30.
What Causes Vitiligo?
Experts still aren’t sure what causes vitiligo, which affects an estimated 1% of the world’s population. The American Osteopathic College of Dermatology notes that it’s suspected to be an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body’s own immune cells attack otherwise healthy cells. In the case of vitiligo, white blood cells destroy pigment-producing melanocytes. People with vitiligo also appear to be more likely to develop other autoimmune conditions, including thyroid disorders and diabetes.
How Is Vitiligo Treated?
There are many vitiligo treatments, each with varying degrees of effectiveness and side effects to consider. In some cases, light therapy may help restore color, while corticosteroids and other medicated skin creams may also be effective. If the vitiligo doesn’t respond to these methods, other more invasive treatments such as skin grafting may be explored.
As an alternative to surgery, our practice offers an advanced laser treatment to help regain skin pigmentation. While there is no cure for vitiligo, this state-of-the-art therapy can reduce the severity of depigmentation and help you regain your confidence. In a small study performed at a Veterans Affairs medical center in Florida, patients who received laser treatment for their facial vitiligo experienced more than 75% repigmentation over several weeks. If vitiligo is taking its toll on your mental and emotional health, don’t hesitate to contact our Atlanta vitiligo treatment specialists at Olansky Dermatology & Aesthetics. Our team can work with you to explore treatment options that will help restore your confidence and reduce the appearance of your depigmentation. To schedule an appointment, call (404) 355-5484, or book one with us online.